Introduction
The public expenditure occupies a special importance in the economic and financial studies, considering it represents the management which is used by the states in order to achieve what they look forward regarding progress and development in all life's sides. The expenditure policy reflects the setting up goals by the government in order to raise the national economy push the development wheel and achieve the economic stability. The structure of public expenditure in Iraq includes disparity in achieving the economic stability, so the effects on development's variables in Iraq should be found. For this reason, the paper is divided into three parts. The first part includes methodology of the paper. The second part deals with the practical side of the paper by analysis the structure of public expenditure in Iraq, analysis inflation phenomenon, analysis unemployment phenomenon, and analysis the effect of public expenditure on both unemployment and inflation regarding the last part, it is dedicated for conclusions and recommendations.
The problem of paper: the structure of public expenditure in Iraq includes a big distortion because the operational consumer expenditure overshadows the investment expenditure. This reflects its effect on the economic development and stability.
The importance of the paper: the importance of paper determines in a way that the public expenditure considers one of the most important financial policy tools which through its balanced between consumption and investment, there will be contribution in building stable economy especially that most of the Iraqi society needs are satisfied through the public expenditure because the great contribution of the government and its great interference in economy.
The goal of paper: the paper aims to find the effects public expenditure in Iraq on some total economy variables in achieving the economic stability.
Hypothesis of the paper: the paper adopts a hypothesis which says that the policy of public expenditure varies in its ability to achieve the economic stability according to the difference of economic conditions.
Echo of the paper: the locative limits of paper represents the policy of expenditure in Iraqi economy and the temporal limits includes the period from 2003 to 2014.
The fact and analysis of the structure of public expenditure in Iraq
We find that public expenditure in Iraq since 2003 and after it increased whether it serves the public sector or the private sector (by moving the market wheel …. etc.) because of the rising of oil prices globally during the period of research and because of rebuilding infrastructure. But there was an economic and political situations and other impediment which were imposed on Iraq and prevented to achieve the drawn goals of public expenditure, we can see table 1 which clarifies the public expenditure in the stated period.
It also clarifies the rate of expenditure’s growth and the total domestic product in the current price, where the public expenditure is based on billion dinars.
Table 1
|
Year |
Actual public expenditure (1) |
Growth rate % (2) |
Gross domestic product (GDP) in constant prices (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2003 |
1982548 |
- |
26990.40 |
|
2004 |
32117491 |
93.82 |
41607.80 |
|
2005 |
26375175 |
-21.77 |
43438.80 |
|
2006 |
38806679 |
32.03 |
47851.40 |
|
2007 |
39031232 |
0.57 |
48510.60 |
|
2008 |
59403375 |
43.3 |
51716.60 |
|
2009 |
52567025 |
-13.00 |
54721.20 |
|
2010 |
70143201 |
25.04 |
57751.60 |
|
2011 |
78757666 |
10.95 |
63650.40 |
|
2012 |
105139575 |
25.09 |
71680.80 |
|
2013 |
119127556 |
11.74 |
75685.80 |
|
2014 |
83556225 |
-42.57 |
75304.00 |
The references of table 1: column 1 ministry of finance, budgetary service, different years; column 2 prepared by the searcher; column 3 ministry of planning, economic models service, different years
Figure 1 represented the public expenditure in the period (2003-2014).
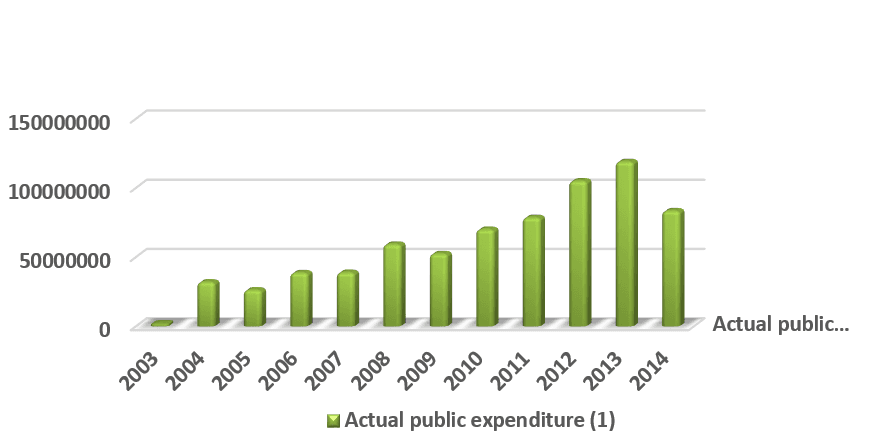
Fig. 1. Public expenditure in the period (2003-2014)
The public expenditure was in 2003 1982548 billion dinars because of the current circumstances in that period, whereas the total domestic product in that period was assessed 2699040 billion dinars.
After a year passed and determinatively 2004, we notice that public expenditure increased reaching 32117491 billion dinars because of improvement in the conditions of Iraqi economy, when the increase in public expenditure was for moving the Iraqi economy wheel. Furthermore, the rate of expenditure growth in the same year becomes 93,82. In 2005 the public expenditure decreased to 263751 billion dinar and the rate of growth was -21,77 in the same year. Then, in 2006-2008 it returned to increase.
The total domestic product was also high, so it reached in 2008 to 5171660 billion dinars. Then, the public expenditure decreased in 2009 reaching 52567025 billion dinars, with a negative growth rate -13,00.
In 2012, we noticed raising in public expenditure reaching 105139575 billion dinar, this is because of the raising of oil imports and also the raising of oil price globally, this is from one side and from another side because of the security situations which Iraq underwent and still when the situation requires to increase the expenditure on the defense and the security in order to improve the security situation, and also increasing the expenditure on salaries, infrastructures and investments projects. We also notice that the total domestic product in 2012 arrived to 7168080 billion dinars, then the public expenditure increases reaching 119127556 billion dinars in 2013, but it lowers in the next year to 83556225 billion dinars because of the current circumstances [1, p.5]. In general, we notice that total domestic product and public expenditure is in increasing during this period.
Analysis the commercial expenditure (operational) and the investment expenditure in Iraq in the period 2003-2014
The public expenditure structure is known in Iraq with a case of a significant variation between both sides of expenditure (current and investment) when the great rate of public expenditure is a consumption current expenditure at the expense of the rate of investment expenditure. In fact, the wide gap between expenditure’s two halves in favor of current expenditure can’t be adopted by the possibility of achieving high growth rates especially under the reconstruction conditions and achieving development requirement and economic stability.
The increasing of current expenditure should cover to the increasing of total consumer demand at the expense of regression what is allocated to the investment expenditure, and for analysis public expenditure (current and investment), we can see table 2.
Table 2
The amount of operational expenditure and investment expenditure in Iraq in the period (2003-2014) billion dinar
|
Year |
Actual public expenditure |
Investment expenditure |
|---|---|---|
|
2003 |
1784293 |
198254 |
|
2004 |
29102758 |
3014733 |
|
2005 |
21803157 |
4572018 |
|
2006 |
23778999 |
6027680 |
|
2007 |
31308188 |
7723043 |
|
2008 |
47522700 |
11880675 |
|
2009 |
42053620 |
10513405 |
|
2010 |
54003334 |
16130866 |
|
2011 |
60925554 |
178321129 |
|
2012 |
75788624 |
29350953 |
|
2013 |
78746806 |
40380750 |
|
2014 |
76741675 |
35450452 |
The references of table: ministry of finance, budgetary service, different years
It is noticed from table 2 that the operational expenditure occupied a privileged position of the total public expenditure and the reason returns to the great interest of public sector during this period more than their interest of private sector. The operational expenditure is a consumer expenditure. It should be noted that Iraq doesn’t characterize with flexibility in the productive apparatus because of wars’ destruction and the economic blockade which was imposed on Iraq which disrupt the productive apparatus, results in increasing the consumer expenditure [4, p.82].
The figure 2 represented operational and investment expenditure in the period 2003-2014.
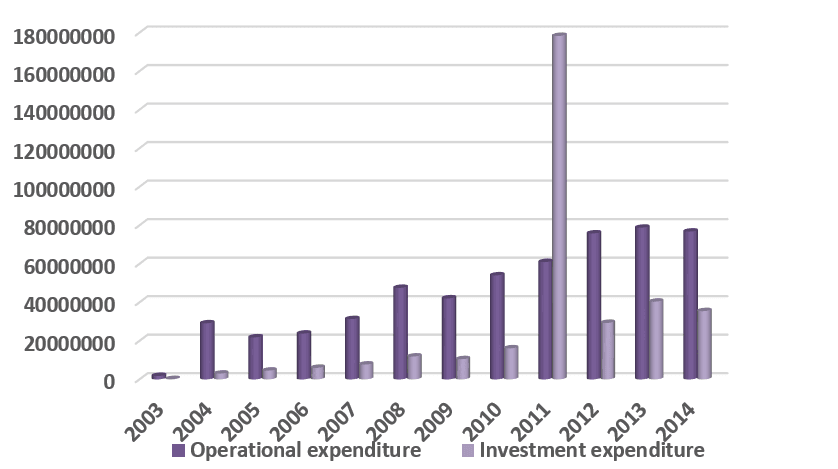
Fig. 2. Operational and investment expenditure in the period (2003-2014) (Reference: prepared by the researcher depending on table 2)
We find that operational expenditure in 2003 reached to 1784293 billion dinars, and in 2004 it increased to 29102758 billion dinars because of the increasing of state institutions’ demand for employees, therefore increasing the wages and salaries. It reached in 2010 to nearly 54003334 billion dinars, whereas it recorded the highest rise in the operational expenditure along the period of research in 2013 reaching 78746806 billion dinars because of the explosive budget and the pressure which were imposed from the political actors to increase the operational expenditure. Then it decreased in 2014 reaching 76741675 billion dinars.
Generally, we notice that the operational expenditure is in a growth along the period of research.
We find that investment expenditure, which consider one of the most prominent instruments of financial policy isn’t given a great importance. It reached in 2003 approximately 198254 billion dinars. The reason of reduction in the rate of investment expenditure on public expenditure is the occupation of Iraq, the rise of violence and terrorist attacks which lead to stop the reconstruction in Iraq, and what was allocated for investment expenditure from the total of budgets' allocations for the following years for 2003 is only a small percentage of public expenditure. It reached in 2004 approximately 3014733 billion dinars. In 2005, it was allocated in the budget for investment expenditure for reconstruction Iraq and recycling the Iraqi economy wheel an amount of 4572018 billion dinar and only 20% was spent from it. This has led to continue the structure imbalance represented by the weakness of local commodity production base especially in industrial and agricultural sectors whereby the role of these sectors retreated largely in the generation of domestic product, whereby it was supposed that financial policy has to allocate which it isn't spent in order to provide the recovery needs of these sectors, when the lack of fuel and energy, which their problems haven't solved yet, considers one of the factors which worsens these sectors. Furthermore. Non-availability of loans and liquidity with regard to the establishment of public sector (industry and agriculture). this explains the persistence of rural character and non-productive for economic policy directives, which contributed in the decline of commodity sectors as a result of concentration of state resources on oil export revenues which constitute more than (95%) of country's budget and neglect the other sectors like industry, agriculture and others, consequently, the weakness of the national production system and the dependence on imports from abroad [5, p.44].
We find that the highest volume of investment expenditure was in 2011 reaching 178321129 billion dinars because of the rise of oil prices, in return the operational expenditure was lower in the same year. But the investment expenditure shrinks quickly to the reduction reaching in 2014 to 4293966 billion dinars.
Analysis the phenomenon of inflation in the Iraqi economy in the period (2003-2014)
The inflation in the Iraqi economy during the stated period characterized by volatility sometimes it arises too high and another time it lowers on this basis, inflation in Iraq can be divided during the study period into two periods. The first one is the period of high inflation (2003-2008). This new trend in the rise of inflationary comes from many reasons which were caused by the pressure of aggregate demand that has contributed significantly in maximization the risks of inflation caused by withdrawal the expenditure in general and consumer government expenditure in particular (with the inefficiencies of large productive sectors, particularly in the field of agricultural and industrial activity). from the above structural shortcomings have existed because of the underdevelopment in the economic structure, increasing the reliance on imports and exacerbation of external indebtedness, in addition to the economic, political and security upheavals, after war [9, p.2].
It indicates from table 3 that the rate of inflation reached in 2003 approximately 33.6% then it declined slightly in 2004 reaching 27.0%. Then it has grown rapidly to reach its highest level in 2006 reaching 53.1% because of the raising prices of oil derivatives when the government reduced the support for it.
Table 3
Rate of inflation in Iraq through the period (2003-2014)
|
Year |
General Standard number (CPI)100=2007 |
Inflation rate % |
|---|---|---|
|
2003 |
42.8 |
33.6 |
|
2004 |
36.4 |
27. |
|
2005 |
49.9 |
37.0 |
|
2006 |
76.4 |
53.1 |
|
2007 |
100.0 |
30.9 |
|
2008 |
112.7 |
12.7 |
|
2009 |
112.1 |
8.3 |
|
2010 |
125.1 |
2.5 |
|
2011 |
132.1 |
5.6 |
|
2012 |
140.1 |
3.1 |
|
2013 |
142.7 |
1.9 |
|
2014 |
145.9 |
2.2 |
The reference of table 3: ministry of planning, general statistical organization, directorate of national accounts
Using information of table 3 to drawing figure 3.
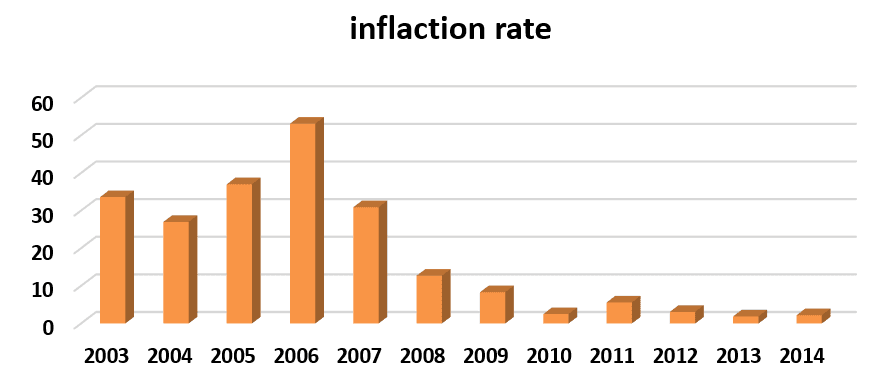
Fig. 3. The rate of inflation in Iraq through the period 2003-2014
The second period 2009-2014. This period underwent low inflation rates don't exceed one decimal point since the inflation rate in 2009 reached 8.3%, then it decreased to low level in 2010 reaching 2.5%. The two years 2013-2014 underwent a great reduction reaching 1.9% and 2.2% respectively, that's because the global financial crisis which afflicts the world economy and leads to decrease the imported goods consequently, the rate of inflation has declined.
Furthermore, the availability and low prices of petroleum products, and the global decline of primary commodity prices particularly food commodity prices according to the food and agriculture organization of the united nations (FAO) against backdrop of availability of offered thing and decline of global demand (Central Bank Economic Report, 2005).
Analysis the phenomenon of unemployment in the Iraq economy for the period (2003-2014)
Statistical estimates indicate that the scale of unemployment in Iraq is great. There is no doubt that the public sector alone cannot afford an additional opportunity job, the private sectors are labor- invasive and suffer from under employment problem. About the weakness of domestic private sector, the government finds an embarrassment in finding a necessary opportunity job to solve the unemployment problem [2, p.48].
The most prominent characteristics of Iraqi labor market is the high of display's growth rate from work as result of the high rates of population growth and labor force under the slow of demand growth for work which results from several factors, notably, the ability to increase the aggregate supply tailored to the total effective demand, consequently, growth in import volumes by more than export.
That is means declining investment opportunities and capital formation as result of exit of foreign currency. This have the effect if increasing difficulties facing the Iraqi economy to direct economic activities in the fields that achieve the determination and economic stability.
Table 4
The rate of unemployment in Iraq in the period (2003-2014)
|
Year |
Unemployment rate% |
|---|---|
|
2003 |
28.10 |
|
2004 |
26.80 |
|
2005 |
17.90 |
|
2006 |
17.50 |
|
2007 |
11.70 |
|
2008 |
15.30 |
|
2009 |
14.00 |
|
2010 |
12.00 |
|
2011 |
11.00 |
|
2012 |
11.90 |
|
2013 |
12.10 |
|
2014 |
12.70 |
Reference of table 4: republic of Iraq. Ministry of planning and cooperation development, department of economic models, different years using the data of table 4 can be gate figure 4
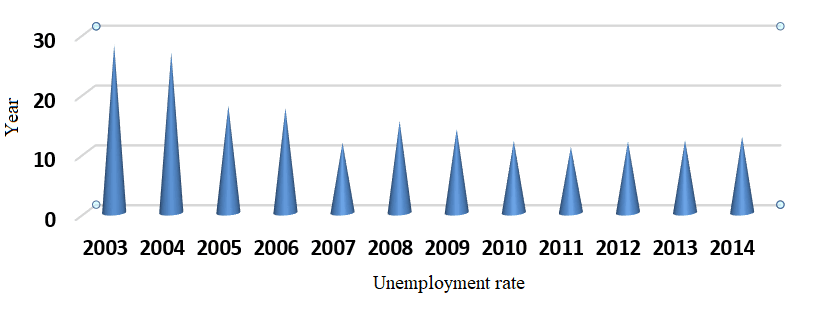
Fig. 4. The rate of unemployment in Iraq through the period (2003-2014)
From table 4, we notice that unemployment's rate in Iraq is high in comparison with the other advanced countries. Despite this high, we notice that it is in generally in fluctuation as a result of the politicizes which was used to tackle unemployment in Iraq was in 2003 reaching 28.10% as a result of occupation of Iraq and its consequences of crises and problems.
These include the interim coalition government's demobilization of the Iraqi army, disturbance of security situation and increasing of looting plunder and sabotage and many other problems [3, p.71].
Then, the rate of unemployment is declining as a result of the improvement in the labor market and increasing the demand for labor reaching in 2007 nearly 11.70% this rate considered the lower through the period 2003-2007. But the rate of employment is rising and falling after 2007 that is rises to 15.30% in 2008, but it soon fell reaching 11.00% in 2011. This rate represents the lowest rate during the period 2003-2014. This decrease is due to the state's interest in reducing the rate of unemployment by hiring large numbers in public sector institutions and in the army and police crops. Furthermore, the numbers of labor migration to work outside Iraq increased. Then, the rate of unemployment increased reaching 12.70% in 2014 [2, p. 43].
Analysis the role of public expenditure in the effect on both unemployment and inflation in the period 2003-2014
We notice through the data of table 5 that public expenditure rising steadily long duration of search despite its flection from year to year because of the expansion of the role of the government and its intervention in various fields of life. This reflected in achieving the economic stability through several indicators, including unemployment and inflation. This effect is observed when public expenditure increases as shown in table 5. We find that the rate of unemployment and inflation decreases to different levels public expenditure was low in 2003 reaching 1982548 billion dinar and unemployment was in its highest rate in the same year reaching 28.10%, and the rate of inflation was also 33.61%.
Table 5
The rate of public expenditure and the rate of unemployment and inflation
|
Years |
Public expenditure (1) |
Unemployment (2) |
Inflation (3) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
2003 |
1982548 |
28.10 |
33.6 |
|
2004 |
32117491 |
19.90 |
27.0 |
|
2005 |
26375175 |
17.90 |
37.0 |
|
2006 |
38806679 |
17.50 |
53.1 |
|
2007 |
39031232 |
11.70 |
30.9 |
|
2008 |
59403375 |
15.30 |
12.7 |
|
2009 |
52567025 |
14.00 |
8.3 |
|
2010 |
70134201 |
12.00 |
2.5 |
|
2011 |
78757666 |
11.00 |
5.6 |
|
2012 |
105139575 |
11.90 |
6.1 |
|
2013 |
119127556 |
12.10 |
1.9 |
|
2014 |
83556225 |
12.70 |
2.2 |
Reference
Ministry of finance, budgetary services, different years.
Republic of Iraq, ministry of planning and cooperation development, department of economic models, different years. Ministry of planning, general statistical organization, directorate of national account.
When public expenditure increased in 2004 reaching 32117491 billion dinars, the rate of unemployment decreased reaching 26.80% and the rate of inflation also decreased reaching 27.0%. In 2011, public expenditure was 78757666 billion dinar and rate of unemployment in this year 11.00% and it's the lowest rate of unemployment long duration of search because of raising investment expenditure significantly reaching 60925554 billion dinars. Inflation rate also reached that year 5,6%, public expenditure has its highest level in 2003 reaching 119127556 billion dinars. Unemployment rate in that year was 12,10%. Inflation rate was in its lowest level long duration of searching, reaching 1,9%.
Then, public expenditure decreased in 2014 reaching 83556225 billion dinars. This had reflected on the rate of employment, its increased reaching 12,70% and the rate of inflation also increased reaching 2,2%. This shows the role and the effect of public expenditure on both unemployment and inflation consequently the economic stability.
Conclusions
- The paper indicates that there is expansionary expenditure policy through the period of paper as a result of increasing oil revenues and increasing the price internationally.
- There is a structural multifunction in the distribution of public expenditure between operational and investment expenditure when the operational expenditures have the greatest portion.
- The inflation in the Iraqi economy characterized with fluctuation (rise and fall during the search period).
- The unemployment in the Iraqi economy also characterized with fluctuation because of rise and fall during the search period.
Recommendations
- Adoption of fiscal policy which prioritizes the expansion in investment expenditure in order to achieve an annual growth rate.
- Direct the investment expenditure as a sectoral need with focus on vital sectors (agriculture and industry) to accommodate the largest number of workers.
- Encouraging the participation of the private sector and producers in providing job creation through government support in its different shapes (loans, grants, and exemption) which contribute to solve unemployment problem.
- Subjecting the public expenditure to the criteria of economic feasibility in order to achieve efficiency and effectiveness in using public resources.

.png&w=640&q=75)