Introduction
The problems and effectiveness of teaching a foreign language in universities have occupied an important place in the discussions of the scientific community for more than a decade. Relevant in recent years is not only the search and testing of modern pedagogical methods of teaching a foreign language, its various levels and industry variations, but also a combination of methods, the use of new computer environments and tools.
The development of critical thinking of students has been actively engaged in the world for a long time, for example, in the USA, teaching critical thinking as a separate discipline is a generally recognized requirement of the standard of higher education [1]. At the moment, a significant amount of specialized test material has been developed to determine the level of critical thinking for exams, the results of which are one of the most important indicators of student learning success. In our country, the interest of the scientific community in the study of critical thinking has grown in the last decade.
In this article, I consider my experience in developing critical thinking in the framework of teaching a foreign language to students of non-linguistic specialties.
The main features or characteristics of critical thinking were proposed by D. Dewey, B. Bloom, D. Halpern, P. Bonnie, and others.
And also to determine the formation of the following rational abilities of critical thinking in the context of pedagogical science:
- the ability to work with information: collecting information, "active reading", analyzing the quality of information;
- consideration of the situation (learning task, problem) as a whole, and not its individual moments;
- identification of the problem, its clear definition, clarification of its causes and consequences, drawing logical conclusions;
- development of one's own position on the problem under study, the ability to find alternatives, the ability to change one's opinion depending on the obvious, etc. [2]
In Kazakhstan, a number of scientists define critical thinking as follows:
Lifanova T.Yu. defines "critical thinking as an intellectually organized process aimed at active thinking, application, analysis, generalization or evaluation of information obtained or created through observation, experience, reflection, reasoning or communication as a guide to action or the formation of beliefs” [3].
Some aspects of the formation of critical thinking are considered in the works of Karagozina M.I. Her research is based on the second module of the Program of advanced training courses for teachers of the Republic of Kazakhstan – training in critical thinking. In his study Karagozina M.I. adheres to the following definition "critical thinking is a disciplinary approach to comprehending, evaluating, analyzing and synthesizing information obtained as a result of observation, experience, reflection or reasoning, which can later serve as a basis for action" [4].
During my research I have the questions like these: How to develop critical thinking skills? Will it be effective in the English discipline? What kinds of exercises are the best for developing these skills? What methods should I use?
The hypothesis of research work
Students of non-linguistic specialties will successfully develop critical thinking skills in the English language if:
- when teaching a foreign language, the technology of developing critical thinking using authentic texts will be used;
- teaching will use such techniques and exercises that not only increase the level of language proficiency, but also force students to perform such mental operations as analysis, comparison, comparison and others.
The technology “Development of critical thinking” was developed by the International Reading Association of the University of Northern Iowa and Hobard and William Smith Colleges (authors: Ch. Temple, J. Steele, K. Meredith, Sc. Walter) .
A lesson on the technology of critical thinking compositionally involves 3 stages: a call (evocation), comprehension of the content (realization of meaning), reflection (reflection). At the stage of the “call”, the goals of cognition are determined, at the stage of “understanding the content”, an active search for information is carried out, at the stage of “reflection” – reflection and evaluation of the studied material, the birth of new knowledge [5].
In the experiment took part 1st year bachelor degree students (non-linguistic specialties) in a “foreign language” class.
On the diagram below we can see the results of the tests for level of critical thinking at the beginning and at the end of experiment.
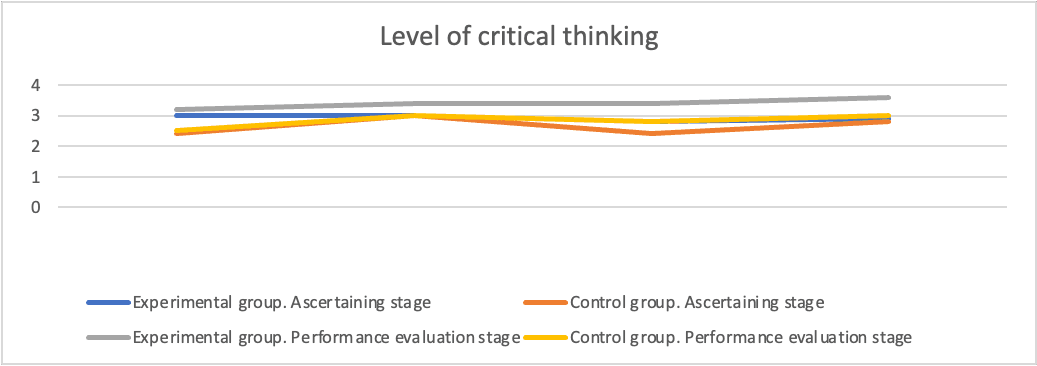
Fig.
Now I want to show some exercises which I have been used during experiment.
- K-W-L charts are three-part graphic organizers to engage, guide and review. The picture below shows an example table for this exercise. The advantage of this strategy: it allows students to analyze the topic of an authentic text, and understand what they know, want to know and what they have learned.
- Forecasting by illustration. Students are given a drawing or illustration. They put forward their theories and assumptions about what is depicted and how it relates to the topic of the lesson.
The exercises above I used for the “Call” stage.
For the next stage “Realization of meaning” I have used these kinds of exercises:
- Venn Diagram. I have used it when I turn students audio or video for theme of the text and they read and listened, then they fill in difference between the information in the text and in the audio.
- "Six Thinking Hats". In this exercise students should mark by color: White-information and facts. Yellow hat – positive, virtues, pluses. Black hat – criticism - difficulties, dangers, shortcomings. Red hat – emotions and feelings. Green hat-new ideas and creativity. Blue hat: control and management of the thought process for the teacher.
For the last stage “Reflection” I have used these exercises:
- I divide the students into groups of 3. Students had to prepare "Short stories" according to the criteria of the site "fiftywordstories.com" where the main component is the use of a certain (50 words) number of words. For this task, in order to develop critical thinking skills, I prepared a collage for each group on the basis of which they had to compose a text.
- "Tug of War". The students were divided into two groups, the exercise was held in the form of a debate. In this exercise, they voiced all the arguments for and against each of the topics.
Conclusion
The methodology we have considered and the results obtained confirm the hypotheses of pedagogical experiments that the development of critical thinking contributes to more effective mastery of a foreign language. There was a clear increase in the level of critical thinking in the experimental group of students compared to the control group.
The usage of technology for the development critical thinking skills and authentic texts, exercises for them are successfully develop these kinds of skills.

.png&w=640&q=75)