Introduction
In recent decades, nanotechnology has become an essential part of the beauty industry. The use of nanoparticles in cosmetics enhances the texture, durability, and effectiveness of products. However, along with their advantages, nanomaterials pose potential risks to human health and the environment. This article explores the key aspects of nanotechnology applications in decorative cosmetics, their impact on the skin, as well as safety and regulatory concerns.
Use of nanoparticles in cosmetic products: advantages and potential consequences
Nanoparticles are particles smaller than 100 nm, possessing unique physicochemical properties. In cosmetics, they are used to improve product texture and longevity, ensure uniform pigment distribution, enhance the penetration of active ingredients, and create a soft-focus effect by scattering light.
The most commonly used nanomaterials in decorative cosmetics include:
- Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) and zinc oxide (ZnO) – used in sunscreens and foundation products.
- Nanogold and nanosilver – applied in anti-aging and antibacterial products.
- Liposomes and nanosomes – capsules designed to deliver active ingredients into deeper layers of the skin.
Despite their advantages, there are several potential risks. Some studies indicate that nanoparticles can penetrate the skin, cause oxidative stress, damage cells, and contribute to inflammatory processes. More details are provided in Table.
Table
Nanomaterials in Cosmetics
Nanomaterial | Application | Potential Risks |
Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) | Sunscreen products, foundation | Skin penetration, oxidative stress |
Zinc Oxide (ZnO) | Sunscreen and antiseptic products | Safe, but requires monitoring |
Nanogold | Anti-aging and decorative cosmetic products | Skin hypersensitivity, potential toxicity |
Nanosilver | Antibacterial components in cosmetics | Antibacterial resistance, toxicity |
Liposomes | Delivery of active ingredients into the skin | May alter properties of active ingredients |
Examples of nanoparticle use in decorative cosmetics
Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂) is widely used in decorative cosmetics due to its properties: it provides coverage, light scattering, resistance to external influences, and UV protection. Below are examples of its application in various products:
1. Foundations, BB/CC Creams:
- Estée Lauder Double Wear Stay-in-Place Foundation – contains TiO₂ as a sun protection component and for full coverage.
- IT Cosmetics Your Skin But Better CC+ Cream – CC cream with high SPF due to titanium dioxide.
2. Face Powders:
- Laura Mercier Translucent Loose Setting Powder – setting powder with TiO₂ for a matte effect and sun protection.
- MAC Studio Fix Powder Plus Foundation – compact powder with titanium dioxide for long-lasting coverage.
3. Concealers:
- NARS Radiant Creamy Concealer – concealer with TiO₂ for a light-reflecting effect and blemish coverage.
- Tarte Shape Tape Concealer – contains TiO₂ for full coverage and UV protection.
4. Lipsticks and Lip Glosses:
- Chanel Rouge Coco Lipstick – contains TiO₂ for rich color and sun protection.
- Maybelline SuperStay Matte Ink – matte lipstick containing TiO₂ for pigment density.
5. Eyeshadows:
- Urban Decay Naked Palette – some shades contain TiO₂, ensuring longevity and color intensity.
- Huda Beauty Obsessions Palette – pigmented eyeshadows using TiO₂ for even color distribution.
6. Eyeliners and Eye Pencils:
- NYX Jumbo Eye Pencil in Milk – white pencil containing TiO₂ for high pigmentation and full coverage.
- Stila Stay All Day Waterproof Liquid Eye Liner – liquid eyeliner with TiO₂ for durability and precise lines.
Titanium dioxide plays a crucial role in decorative cosmetics–not only enhancing color and longevity but also providing UV protection, making textures softer and more even.
Zinc Oxide (ZnO) in decorative cosmetics
Zinc oxide is widely used in decorative cosmetics due to its properties: it provides UV protection, has antiseptic effects, and contributes to texture durability. Below are examples of ZnO applications in decorative cosmetics:
1. Foundations, BB/CC Creams:
- BareMinerals Original Foundation – mineral powder foundation with ZnO for natural coverage and UV protection.
- La Roche-Posay Anthelios Mineral Tinted Sunscreen – tinted cream with zinc oxide providing SPF 50.
2. Face Powders:
- Jane Iredale Amazing Base Loose Mineral Powder – mineral powder with zinc oxide, ensuring mattification and sun protection.
- Colorescience Sunforgettable Total Protection Brush-On Shield – loose powder with ZnO (SPF 50) for skin protection.
3. Concealers:
- Tarte Amazonian Clay Waterproof 12-Hour Concealer – contains ZnO for longevity and additional sun protection.
- RMS Beauty “Un” Cover-Up Concealer – natural creamy concealer with zinc oxide for skin care.
4. Lipsticks and Lip Balms:
- Supergoop! Lipshade 100% Mineral SPF 30 – contains ZnO for UV protection of the lips.
- Ilia Balmy Tint Hydrating Lip Balm – moisturizing lip balm with zinc oxide.
5. Mineral Eyeshadows:
- BareMinerals Gen Nude Eyeshadow Palette – mineral-based eyeshadows with ZnO for improved adhesion and durability.
- Alima Pure Satin Matte Eyeshadow – contains zinc oxide, providing softness and even application.
6. Eyeliners and Liquid Liners:
- Ere Perez Jojoba Eye Pencil – natural pencil with ZnO, ensuring smooth application and eyelid care.
- 100% Pure Long Last Liquid Eye Liner – liquid liner with a natural formula, including ZnO.
Zinc oxide is a versatile ingredient used in decorative cosmetics not only as a pigment but also as a UV-protecting and skin-nurturing component.
Nanogold (Colloidal Gold) in decorative cosmetics
Nanogold is used in decorative cosmetics due to its anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and brightening properties. Below are some examples of its application:
1. Primers and BB/CC Creams:
- Guerlain L’Or Radiance Primer – makeup primer with gold particles, adding radiance and hydration to the skin.
- Tatcha The Silk Canvas – primer with gold micro-particles that smooth the skin and give it a healthy glow.
2. Highlighters and Powders:
- Yves Saint Laurent Touche Éclat – concealer-highlighter with golden pigments for a radiant skin effect.
- Dior Nude Air Luminizer – baked highlighter with gold particles for a natural glow.
3. Lipsticks and Lip Glosses:
- Pat McGrath Labs BlitzTrance Lipstick – lipstick with gold micro-particles, creating a metallic effect.
- YSL Rouge Pur Couture Gold Attraction Edition – limited-edition lipsticks with gold coating.
4. Eyeshadows:
- Natasha Denona Gold Palette – eyeshadow palette with gold shades, containing nanogold for intense shimmer.
- Charlotte Tilbury Eyes to Mesmerise in Star Gold – creamy eyeshadow with gold pigments for eye enhancement.
5. Face Masks with a Decorative Effect:
- Peter Thomas Roth 24K Gold Mask – face mask with 24-karat gold for radiance and rejuvenation.
- Chantecaille Gold Recovery Mask – mask with gold particles and anti-aging components.
The use of nanogold in decorative cosmetics not only creates a luxurious visual effect but also provides skincare benefits by improving skin texture and tone.
Nanosilver (Colloidal Silver) in decorative cosmetics
Nanosilver is used in decorative cosmetics for its antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and protective properties. It helps extend the shelf life of products and reduces the risk of irritation, making it ideal for sensitive and problem-prone skin.
1. Foundations and BB/CC Creams:
- SKIN79 Super+ Beblesh Balm BB Cream – BB cream with nanosilver for an antibacterial effect, hydration, and tone correction.
- Jart+ Cicapair Tiger Grass Color Correcting Treatment – color-correcting cream with colloidal silver for skin protection against irritation.
2. Face Powders:
- It’s Skin Babyface Silky Finishing Powder – mineral powder with nanosilver, regulating sebum production and preventing inflammation.
- Innisfree No-Sebum Mineral Powder – loose powder with antibacterial properties, containing nanosilver.
3. Concealers:
- The Saem Cover Perfection Tip Concealer – contains nanosilver, providing both full coverage and antimicrobial protection.
- Missha The Style Under Eye Brightener – concealer with skincare components, including colloidal silver.
4. Lipsticks and Lip Glosses:
- Holika Holika Heartful Moisture Lipstick – contains nanosilver for an antibacterial effect and prolonged lipstick wear.
- Labiotte Wine Lip Tint – lip tint with colloidal silver to prevent bacterial growth.
5. Eyeshadows:
- 3CE Mood Recipe Multi Eye Color Palette – eyeshadows with antiseptic components, including nanosilver.
- TonyMoly Crystal Lovely Eyes – eyeshadow pencil with a caring formula containing silver.
Nanosilver is especially prevalent in Asian cosmetics (South Korea, Japan) as it prevents inflammation, extends product shelf life, and suits sensitive skin.
Liposomes in Decorative Cosmetics
Liposomes are used in decorative cosmetics to enhance the penetration of active ingredients into the skin, provide hydration, anti-aging care, and protection against external factors. They encapsulate beneficial components (vitamins, antioxidants, moisturizing agents) and help deliver them into the deeper layers of the skin.
1. Foundations and BB/CC Creams:
- Lancôme Teint Idole Ultra Wear Foundation – contains liposomal technology for hydration and long-lasting coverage.
- Dior Capture Totale Super Potent Serum Foundation – foundation with liposomal hyaluronic acid and peptides for an anti-aging effect.
- Jart+ Premium BB Beauty Balm – BB cream with liposomes for skin protection and anti-aging care.
2. Face Powders:
- La Mer The Powder – loose powder with liposomes of marine minerals for skincare and protection.
- Sisley Phyto-Poudre Libre – lightweight powder with plant extract liposomes, providing a soft finish.
3. Concealers:
- Yves Saint Laurent Touche Éclat High Cover Concealer – concealer with antioxidant liposomes for a radiant effect and protection against free radicals.
- Giorgio Armani Luminous Silk Concealer – creamy concealer with liposomal hyaluronic acid for hydration and skin rejuvenation.
4. Lipsticks and Lip Glosses:
- Chanel Rouge Coco Flash – lipstick with oil-based liposomes for hydration and lip softening.
- Dior Addict Lip Glow – contains liposomes for deep nourishment and lip protection.
5. Eyeshadows:
- Shiseido Aura Dew – cream eyeshadows with liposomes for a moisturizing effect.
- Chantecaille Luminescent Eye Shade – eyeshadows with silk liposomes and antioxidants for delicate eye skin care.
6. Eyeliners and Pencils:
- Sisley Phyto-Kohl Star Eyeliner – contains liposomes of plant components for eyelid softening.
- Lancôme Le Stylo Waterproof Eyeliner – pencil with moisturizing liposomes for comfortable application.
7. Makeup Setting Sprays:
- MAC Prep + Prime Fix+ – setting spray with vitamin and antioxidant liposomes for makeup refreshment and skincare.
- Clarins Fix’ Make-Up Mist – setting mist with plant extract liposomes for hydration and skin protection.
Liposomal technology allows these products not only to enhance their decorative properties but also to actively care for the skin, making cosmetics more functional.
Using the information provided above, I have created a graph (Fig. 1) that visually demonstrates the use of nanomaterials in decorative cosmetics across different categories.
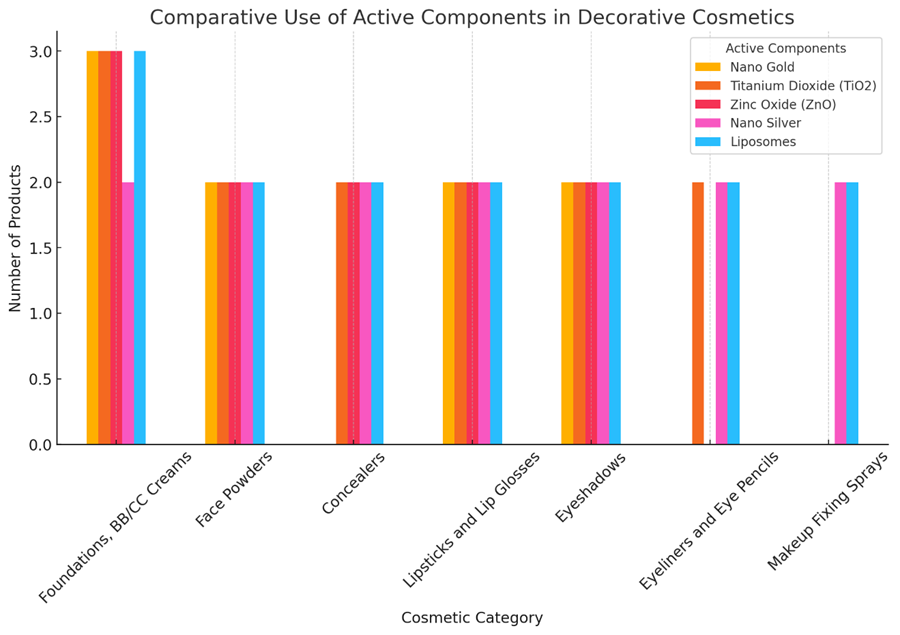
Fig. 1. Comparative use of active components in decorative
Summary of the Comparative Graph (Fig. 1)
1. Leading Active Ingredients:
- Titanium dioxide (TiO₂) and liposomes are the most widely used in all categories of decorative cosmetics. This is due to their ability to provide full coverage, UV protection, and skincare benefits.
- Zinc oxide (ZnO) is also actively used, particularly in face products (foundations, powders, concealers) due to its sun protection and antiseptic properties.
2. High Use of Nanosilver:
- Nanosilver is included in almost all categories except nail polishes. It is particularly in demand in eye, lip, and makeup setting products due to its antibacterial properties.
3. Targeted Use of Nanogold:
- Nanogold is mainly found in foundations, powders, highlighters, and lipsticks, where its primary role is to add radiance to the skin.
4. Diversity of Active Ingredients Across Categories:
- Foundations, BB/CC creams contain the highest number of active ingredients, as they serve both decorative and skincare functions.
- Powders and concealers include a combination of UV filters (TiO₂, ZnO) and antimicrobial agents (nanosilver).
- Eyeliners and liquid liners have a limited number of active components due to formulation requirements for texture and durability.
It can be concluded that active ingredients in decorative cosmetics not only enhance the visual effect but also provide skincare benefits. TiO₂, ZnO, and liposomes are the leaders in application as they combine protective and skincare properties. Nanogold and nanosilver are used in targeted applications, adding antiseptic and brightening effects. Foundations contain the highest number of active ingredients, confirming the trend toward hybrid cosmetics (makeup + skincare).
Impact of nanomaterials on the penetration of active ingredients into the skin
One of the key challenges in cosmetology is delivering active ingredients into the deeper layers of the skin. Nanoparticles significantly enhance penetration due to:
- Reduced particle size, which facilitates transport through the stratum corneum.
- Lipophilicity, which promotes passage through cell membranes.
- The use of carriers, such as liposomes and nanocapsules, providing prolonged release of active substances.
- However, the degree of penetration depends on:
- Skin type and condition (damaged skin is more permeable).
- The chemical composition and size of nanoparticles.
- Exposure duration.
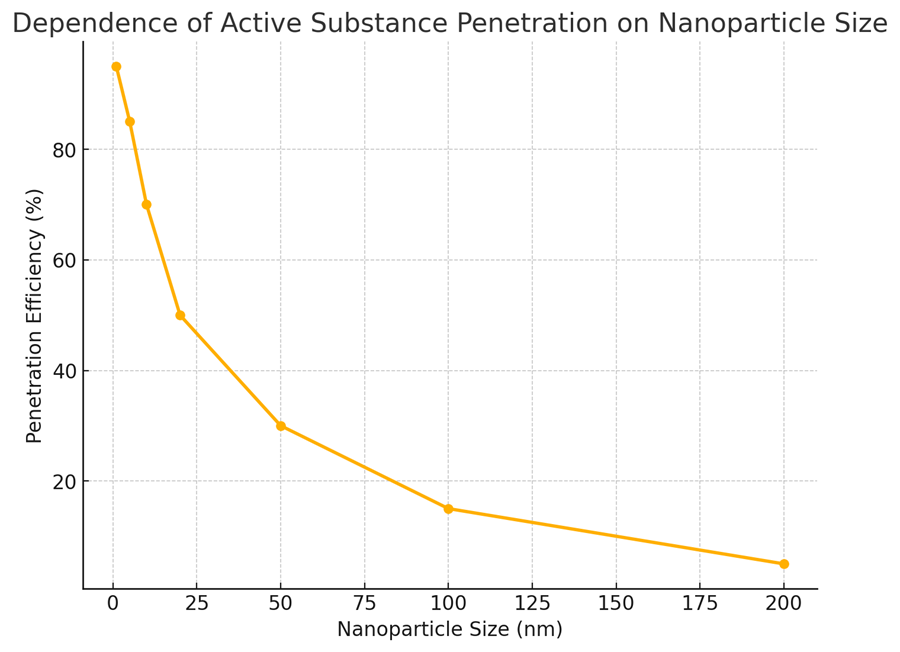
Fig. 2. Dependence of active substance penetration on nanoparticle size
Dependence of active ingredient penetration on nanoparticle size
Analysis of the data (Fig. 2) reveals the following trends:
- Small nanoparticles (<50 nm) have the highest penetration ability – about 80% of active ingredients penetrate the skin barrier. This is due to their small size and high mobility, which facilitates diffusion through the stratum corneum.
- Medium-sized nanoparticles (50–100 nm) exhibit moderate penetration, reaching about 65%. While their penetration ability is lower than that of smaller particles, this size still allows substances to reach the deeper layers of the epidermis.
- Large nanoparticles (100–200 nm) penetrate significantly less, with only 40% of active ingredients reaching the skin. Their size limits passage through intercellular spaces, reducing the efficiency of ingredient delivery to deeper layers.
- Particles larger than 200 nm hardly penetrate the skin, with penetration limited to 20%, which is explained by the physiological barrier of the stratum corneum, preventing large particles from passing through.
Some studies indicate the potential for systemic distribution of nanoparticles, requiring further research and regulatory oversight.
Conclusions from the Graph (Fig. 2):
- The smaller the nanoparticle size, the higher its ability to penetrate the skin, making particles smaller than 50 nm the most effective for delivering active substances.
- Moderate-sized nanoparticles (50–100 nm) maintain a balance between penetration capability and safety, making them preferable for cosmetic applications.
- Large particles (>200 nm) poorly penetrate the skin barrier but can remain on the skin surface, providing protective coatings or visual effects (e.g., in decorative cosmetics).
- The high penetration ability of small nanoparticles may pose risks associated with potential accumulation in body tissues, requiring further research on their safety.
These findings highlight the importance of selecting the optimal nanoparticle size to achieve a balance between active ingredient delivery efficiency and cosmetic product safety.
Regulation and safety of nanotechnology in cosmetics
The safety of nanomaterials remains a subject of debate. Different countries have established various regulatory requirements:
- EU: Regulation (EC) 1223/2009 mandates the labeling of nanoparticles and requires safety assessments.
- USA: The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) recommends additional testing but does not impose strict bans.
- Japan and Australia: Restrictions have been introduced on the use of certain nanomaterials.
Modern safety assessment methods include studies on cellular models and animals, phototoxicity and mutagenicity tests, and monitoring environmental impact.
Conclusion
Nanotechnology offers extensive possibilities for decorative cosmetics, enhancing both effectiveness and functionality. However, its application requires thorough evaluation of potential risks. Regulatory agencies and scientific research continue to study the long-term effects of nanoparticles to ensure consumer safety. In the future, nanotechnology development should be accompanied by strict oversight and the exploration of alternative solutions to minimize possible negative effects.

.png&w=640&q=75)