Mechanical is called the properties of fibers and threads that determine the ratio of different applied forces to the effect. These properties characterize the behavior of fibers and threads during the extraction, processing and use of textiles made from them. When assessing and studying the mechanical properties of textile materials, the concept of a test cycle is used, which includes "load-unloading-rest" [1].
Fiber bundles are interrupted on the DSH-3M dynamometer with a scale of up to 3000 Hz and 20 Hz. A bunch of fibers is attached to clamps with corrugated sponges. The upper removable clip is suspended on a stud attached to the end of the 3rd steel flexible tape, which freely rotates Sector 1 and is fixed with one end. The sector is planted on the 2nd axis, on the same axis the 12th system reinforced by the 15th force and the 14th pendulum system reinforced by the 13th load.
The structure of the DSH-3M is shown below (fig. 1).
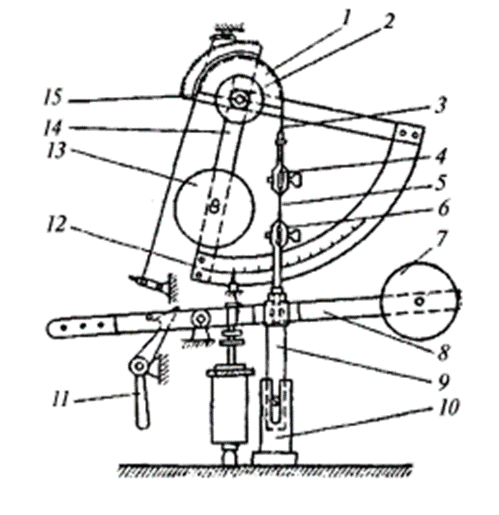
Fig. 1. The structure of the DSH-3M dynamometer
The breaking load of the combed linen is determined on a DKV breaking machine with a pendulum force gauge. The linen is attached to two clamps, one of which is stretched at a constant speed. By moving the thread, the second clamp associated with the needle of the pendulum force gauge moves. The arrow deflects at the same angle as the pendulum and registers the break load on the corresponding scale. The stronger the fiber, the greater the deflection angle of the pendulum force gauge and its needle. Since threads of constant length and mass are tested in the DKV device, the obtained indicators characterize the Relative Strength of the fibers.
The structure of the breaking machine DKV is shown below (fig. 2).
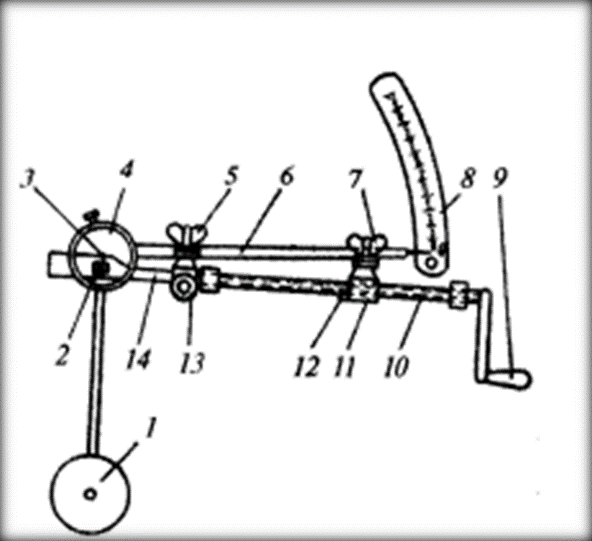
Fig. 2. The structure of the DKV breaking machine
Tests are carried out in accordance with GOST 6611.2-73 on pendulum breaking machine RP-100. When determining the break load by the hanks break method depending on the length of the thread, the number of samples taken from one package must correspond to the one specified in the table.
To determine its breaking load when winding hanks, the ends of the threads in the hanks are tied, (except for threads made of one cotton yarn and chemical fibers with a linear density of no more than 50 textes), slightly twisting their ends. When determining the breaking load of hanks, the drop speed of the lower hook of the machine should be (600±30) mm/min. Hanks are placed on the hooks of the explosive machine in a straightened, untwisted position [2].
The pendulum breaking machine RP-100 is shown below (fig. 3).
Fig. 3. The pendulum breaking machine RP-100
The STATIMAT ME breaking machine is based on a well-known technique for standard yarn. The device complies with all accepted national and international standards and operates in a power range of up to 1000N. The motorist has the ability to check up to 50 bobbins in turn in automatic mode. The scope of application can be expanded using special canvas clamps. Grab test, rowing Test, break check, seam displacement, etc., as well as checking the rolls and cohesion on the ribbons and rivets [3].
The STATIMAT ME breaking machine is shown below (fig. 4).

Fig. 4. The STATIMAT ME breaking machine
The UM-185 portable moisture meter measures the moisture content of fibers, yarns, raw materials, synthetic or mixed textile rolls, yarns and yarns, cotton rolls, wool and fabrics. A system of interchangeable Measuring Probes is used, which determine the electrical conductivity proportional to the moisture content of the material.
The UM-185 portable moisture meter is shown below (fig. 5).

Fig. 5. The UM-185 portable moisture meter
Stelolab device 231B is an instrument for testing the strength and relative elongation of fiber bundles when interrupted. Suitable for cotton fiber, wool and synthetic fibers [4].
The Stelolab device 231B is shown below (fig. 6).

Fig. 6. The Stelolab device 231B
Martindale abrasion abrasive test and peeling tool is designed to test the wear test and peeling of different textiles. First, the round sample is placed on the grinding head and comes into contact with the standard wool cloth abrasive attached to the grinding table under the specified pressure. It is then subjected to multidirectional Translational friction according to the LISSAJU trajectory (synthesized by two mutually perpendicular resonant movements). If the circular sample rubs within the specified time, the device will automatically stop. With this tool, two tests can be obtained:
- textile peeling test;
- textile wear resistance test.
The textile peeling test can also be applied to knitwear and knitted materials. During this process, textile patterns and friction canvases rub against each other on a flattened platform, forming certain geometric shapes. After that, we need to compare the damaged samples and the standard ones.
Five levels according to the degree of peeling described in the table (table).
Table
|
1. |
No peeling |
|
2. |
Light peeling |
|
3. |
Normal peeling |
|
4. |
Hard peeling |
|
5. |
The hardest peeling |
To test the wear resistance of Textiles, it is necessary to attach fabric samples to the flattened platform and make friction with a friction sheet attached to the flattened head. We can obtain the wear resistance of the fabric through the degree of damage and loss of mass of the sample, as well as changes in its appearance under the guidance of atomic absorption spectrometry.

.png&w=640&q=75)